Background
- The term Romanesque means “Roman Like”
- From the 11th-14th Century
Social Change
- Dark Ages: After the collapse of the Roman Empire, Europe was in despair.
- Judgement Day 1000AD– Bible predicted the end of the world.
- Afterwards, Europe was then in peace- this led to better farming & growth in cities.
- Feudal System – A pyramid in society that separated the wealthy from the working class.
- Learning & Education increased
- The Church – The powerhouse of Europe both politically and spiritually.
Crusades & Relics
- Crusades were a christian army of brutal campaigns of violence and self-interest against other religions.
- The Church would usually profit from these crusades.
- They brought back many items and distributed them to churches around Europe.
- People believe the relics had powers to cure.
- A relic is a part of a deceased holy person’s body or a belonging kept as an object of reverence. (example: pieces from the cross, clothing or bones).
Definition: Relics are
objects associated with
Jesus or a Saint.
Relic of Saint Foy
Image from https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/st-foys-golden-reliquary
"St. Foy was a Roman girl martyred in the town of Agen as part of the Diocletian persecutions in 303 AD. Legend holds that the twelve-year-old was first placed on a red hot griddle, and when holy intervention stopped that from killing her, she was beheaded. After death, her relics performed the usual assortment of miraculous cures and visions.."
Pilgrimages -
Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela
Image from http://www.goodwalkingbooks.com/camino.html
- People set out on religious journeys to visit these relics.
- Bones believed to belong to apostle St. James were preserved in a tomb at Santiago de Compostela.
- There were 4 major routes from France - many monasteries along the route held holy relics.
- The increased taxes helped the church help create large impressive churches & began Romanesque Architecture.
Romanesque Architectural Features
• Thick blocky stone walls
• Rounded Arches – on doors, windows and as ornamental arcades on walls.
• Stone Roofs – technical innovations included stone vaulting – it insulated against fire and greatly improved acoustics.
• Excessively wide walls – to carry the weight of the stone roofs.
• Cruciform Shape – Sainte Lazare in Autun, France
• Small Narrow Windows – as large windows would have weakened the walls – this resulted in dark interiors.
• Rounded Interior Pillars
• Radiating Chapels - St. Mary Magdelene in Vézelay
Floor Plan
Nave: Runs from the entrance portal to the centre of the church
Transept: Runs north to south, perpendicular to the nave.
Crossing: The area where the transept meets the nave
Choir and Apse: Main Altar Area
Ambulatory: An arcaded gallery for pilgrims to walk around the main altar (apse)
Side Aisle: Separated from the central nave by a row of arches(arcade) supported by rectangular piers
Radiating chapels: Smaller chapels (often hold a relic) situated at the side of altar (apse)
Vault: An arched stone ceiling extending from wall to wall (or the nave/aisles).
Barrel Vault:A long arch forming a semi-circular roof vault over a rectangular space.
- This was the first method tried, the heavy stones pressed down causing the semi-circular arches to flatten and the walls collapse. This problem was known as outward thrust.
Groin Vault: Formed by the intersections of two barrel vaults and usually square in plan
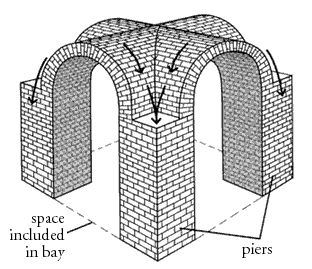

Column: A cylindrical upright support
Pier: An upright support for supporting arches
Portal: Entrance to the church situated at its west end.
Romanesque Sculpture
- Used to teach the illiterate public about Bible stories & about religious icons.
- Subject matter: the theme of death and the grotesque, floral and animal motifs appear as decoration in Romanesque sculpture.
- To display the importance & wealth of the church
- Sculpture was mostly made to fit in with the existing structure of the Church. Hence the reason most human figures are distorted to fit into the frame of the area around them.
Types of Relief
- Low Relief - Less than 50% of the background is remove
- High Relief - More than 50% of the background is removed.
Main locations of sculptures in Romanesque Church
- Capitals: Decorated carving between the top of a column and the weight it is supporting. Area used for depictions of Biblical stories.
2. Tympanum/ Tympana: Semi-circular or triangular decorative wall surfaces over the main portal of a church, secured by a lintel and arch. Area usually reserved to depict Christ.
3. Jambs - A side post or surface of a doorway, window, or fireplace.
Area reserved for Icons, usually Saints and Biblical figures.
4. Tympanum is the semi-circular or triangular
decorative wall surface over an
entrance, bounded by a lintel and arch.
____Romanesque Churches____
Sainte-Foy de Conques (France)
- A typical Romanesque pilgrimage church.
- Houses the skeleton (relic) of Sainte Foy still on display.
- Cruciform shape, large nave & 5 radiating chapels

Over the main doors a semi-circular tympanum illustrates the Last Judgement.
Image from Less Stress More Success
Centre: Christ in Heaven
Left: grotesque depiction of Hell and sinners.
Right: heaven & saints
*Originally painted in full colour and some is still visible.
St Magdalene, Vezelay (France)
- Largest Romanesque church in France
- Holds the relic of Mary Magdalene
- Church was rebuilt around 1150 after a devastating fire that killed 1,200 pilgrims
- During the French revolution the exterior suffered, its facade and one of the towers were destroyed.
- Gothic additions made in the 13th c.
Layout:
- Long rectangular shape
- Very small transepts (barely forming cross shape)
- Large porch due to the huge number of pilgrims
Structure
- Nave roofed with groin vaults
- Nave supported by semi-circular arches on massive pillars
- Decorative contrast of dark and light stones on the arches of the nave (ochre & white stone, chequered effect and shows the influence of Islamic architecture)
Tympanum at St Magdalene, Vezelay (France)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dnxm4UQPDTo
Image from Less Stress More Success
Carved Capital
Image from Less Stress More Success
Saint-Lazare of Autun (France)
- Dating from 12th century - with added gothic architecture later on after a fire in 15th century.
- Holds relic of St. Lazarus (the man whom Jesus raised from the dead)
- Sculptures by master sculptor Gislebertus
Gislebertus, a French sculptor, began his career in Cluny Abbey, in France in 1115.
In 1125, he decorated Vezelay & Autun Cathedral with many sculptures, including over 60 capitals, & the famous ‘The Last Judgement’.
He signed his name which was rare for an artist during this time
'Gislebertus Hoc Fecit'
‘Gislebertus made this’
Tympanum Saint-Lazare of Autun (France)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PATkTJhAUhM
The bodies featured not only in this Cathedral, but in most sculptures during this era, were basic tubular shapes, and elongated due to the lack of knowledge about the human anatomy. Priests also insisted on this style, worried that the congregation would be distracted with unsavoury thoughts should the figures appear too human like
Close up of tympanum at Saint-Lazare of Autun (France)
Image from Less Stress More Success
Illustrations by Victoria Maher
Carved Capitals of tympanum at Saint-Lazare of Autun (France)
The Weighing of The Souls
Image from Less Stress More Success
The Suicide of Judas
Image from Less Stress More Success
The Dream of the Magi
Image from Less Stress More Success
2012
Name and discuss in detail the two sculptures illustrated on the accompanying sheet, making reference to the periods in which they were produced, and to their themes, composition and style.
and
Discuss briefly the role of sculpture in a named medieval church/cathedral that you have studied.
Illustrate your answer.
2011
Discuss the ways in which the main architectural and decorative features of
Romanesque churches differ from those of Gothic cathedrals. In your answer name one Romanesque church and one Gothic cathedral, and make detailed reference to scale, structure, layout and decoration.
and
Name and discuss briefly one example of Gothic sculpture that you have studied.
Illustrate your answer.
2010
The Christian church influenced the development of art and architecture during the Romanesque period. Discuss this statement making detailed reference to the structure, layout and decoration of one named church from the period.
and
Name and discuss briefly one example of Romanesque sculpture that you have studied.
Illustrate your answer.
2007
Romanesque sculpture has decorative and narrative functions.
Discuss this statement in relation to two named examples of Romanesque sculpture you have studied. Emphasise the treatment of the human figure in your answer
And
Name a Romanesque church you have studied and discuss briefly the relationship between its architecture and sculpture.
Illustrate your answer.
2005
Answer (a) and (b)
(a) Describe and discuss the characteristics of Gothic sculpture and its relationship to the architecture of the period. Use specific examples.
(b) How does Gothic sculpture differ from the sculpture of the Romanesque period?
Use specific examples.
Illustrate your answer.
2004
In Europe, crusades, pilgrimages and monasticism contributed to the development of Romanesque art and architecture. Discuss this statement, referring in your answer to two specific Romanesque churches and to the origins, development and characteristics of the Romanesque style.
Illustrate your answer.
All notes and images are for personal use only. These images belong to the stated sources, the use of these are for classroom purposes and educational study. The images are from Google search engine, Appreciating Art for Leaving Cert by G&M and Less Stress More Success - Leaving Cert Art History.







No comments:
Post a Comment